Intro to Machine Learning with TensorFlow
Get to know the basics of machine learning and cover the basic steps to train a machine learning model using TensorFlow
Prerequisites
Basic understanding of the Python programming language and knowledge of artificial intelligence concepts.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data to make predictions and identify patterns. Computers traditionally rely on explicit programming. Machine learning algorithms can be divided into two main categories: supervised and unsupervised learning.
Supervised learning
Used when the training data includes labeled examples. The algorithm attempts to find the relationship between the input features (independent variables) and the output (dependent variable), which is known as the "ground truth". Once the relationship has been learned, the algorithm can use this knowledge to make predictions on new, unseen data. Common examples of supervised learning include classification (determining the class of an object based on its features) and regression (predicting a continuous value).
Unsupervised learning
Used when the training data is unlabeled. The algorithm must identify patterns and structure in the data on its own. Common examples of unsupervised learning include clustering (grouping similar data points) and dimensionality reduction (reducing the number of features in the data).
Why TensorFlow in Machine Learning?
TensorFlow (TF) is an open-source software library for machine learning and deep learning developed by the Google Brain team. It is used for implementing and deploying machine learning models, and it provides a comprehensive and flexible platform for developing deep learning applications by combining the computational algebra of optimization techniques for easy calculation of commonly used mathematical expressions.
Some of the important features of TensorFlow are:
The definition, optimization, and calculation of mathematical expressions easily with the help of multi-dimensional arrays called tensors.
A wide range of programming support (Python, C/C++, Java, R) of deep neural networks and machine learning techniques.
Highly scalable features for computation with various data sets both raw and pre-trained.
TensorFlow, as a cloud-based framework, comes with the power of GPU computing and automation management.
Installing TensorFlow
TensorFlow can be installed in Python easily, just like any other module, with a terminal command using pip, the package manager for Python. Open a terminal or command prompt and enter the following command:
pip install tensorflow
Note: This general installation command may not work for all operating systems.
macOS
To install TF that is optimized for Apple's macOS processors (especially M1 and M2) without going through the troubles of using the general installation, the following command is used:
pip install tensorflow-macos
Windows & Ubuntu without GPU
You can install the CPU version of TF on Windows & Ubuntu if you do not have an external GPU installed or wish to use the CPU:
pip install tensorflow-cpu
Note: Training neural networks with CPUs has performance issues in comparison to powerful GPUs.
TensorFlow also provides a high-level API, called Keras, which can simplify the creation and training of machine learning models. You can install Keras using the following command:
pip install tensorflow-keras
Training a Model in TensorFlow
Open Google Colab, create a new Notebook, and run through these basic steps of training a machine learning model using TensorFlow as follows:
Import the necessary libraries
These libraries might include matplotlib (for data visualization), scipy (for scientific and technical computing), numpy, pandas, and others.
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
#Import the following libraries if you need them
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
Load and preview the dataset
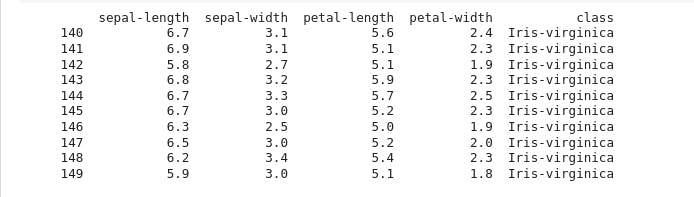
In this example, we'll use the iris dataset, which contains 150 samples of iris flowers with four features (sepal length, sepal width, petal length, and petal width) and three classes (setosa, versicolor, and virginica).
To load the dataset, run:
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x = iris["data"]
y = iris["target"]
To print the last 10 rows of the dataset to preview what it contains, run:
print(data.tail(10))
Split the dataset into training and test sets
The training set will be used to train the model, while the test set will be used to evaluate its performance.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2)
Preprocess the data
This can include normalizing the features and converting the output labels to one-hot encoding.
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x)
Define the model
In TensorFlow, you can define a model using the Keras API. A model in Keras is defined as a sequence of layers, and you can choose from a variety of layer types, including dense (fully connected), convolutional, recurrent, and more. For this example, we'll use a simple fully connected (dense) model with three hidden layers and a softmax activation function in the output layer for the three-class classification problem.
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu', input_shape=(4,)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation='softmax'),
])
Compile the model
Before training, you need to compile the model by specifying the optimizer, loss function, and metrics to use. In this example, we'll use the Adam optimizer, categorical cross-entropy loss, and accuracy as the metric.
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
Train the model
You can train the model using the fit method, which takes the training data and target values as arguments. You can also specify the batch size and the number of epochs (iterations over the training data).
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100)
Evaluate the model
After training, you can evaluate the model's performance on the test data using the evaluate method. This will return the loss and accuracy of the model on the test data.
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print('Test Accuracy:', test_acc)
Make predictions
You can use the trained model to make predictions on new, unseen data using the prediction method.
predictions = model.predict(x_test)
After making predictions, there are several steps that can be taken:
Evaluate the performance of the model
You can use various evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, ROC-AUC, etc. to assess how well the model performed on the test data.
Analyze the errors
You can examine the instances where the model made incorrect predictions and try to understand why the model made those mistakes. This can help you identify limitations or weaknesses in the model.
Improve the model
Based on the analysis of the errors, you can modify the model architecture, change the feature representation, add more data, etc. to improve its performance.
Deploy the model
If the model performs well, you can deploy it to a production environment and use it to make predictions on new, unseen data.
Monitor the performance
After deployment, it's important to monitor the performance of the model and re-evaluate it periodically to ensure that it continues to perform well as the underlying data distribution changes over time.
Iterate the process
The process of building and deploying a machine learning model is iterative, and it's common to go through several rounds of improvement and evaluation before reaching a final, production-ready model.
Conclusion
We introduced the basics of machine learning and covered the steps to train a machine learning model using TensorFlow. TensorFlow is a powerful and flexible platform for developing machine learning models, and the high-level API, Keras, makes it easy to create and train models.
While we only covered the basics, TensorFlow offers a wide range of features and tools for developing more complex models. If you're interested in exploring further, there are many resources available, including the TensorFlow website, tutorials, and documentation.
Machine learning is a rapidly growing field with many exciting applications, and TensorFlow is a great tool for getting started in this area. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting, TensorFlow can help you take your machine learning skills to the next level.
Until we meet again. Same time, same place. Adios!